Achieving Purity in Demin Water Treatment
Introduction
Uncover the marvels of Ultra Pure ZERO TDS Demin Water treatment in this detailed guide. Explore how this method achieves unparalleled water purity crucial for diverse industries.
In today’s world, where water purity is of utmost importance across various sectors such as pharmaceuticals, battery manufacturing, electroplating, dialysis, food processing, and more, the demand for ultra-pure zero Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) demineralized water is ever-increasing. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of ultrapure Demineralized/Deionized (DI) water treatment, the processes involved, and its critical role across different industries.
What is Ultra Pure Demineralized (DI) Water Treatment?
Ultrapure demin water treatment involves the removal of all ions and dissolved solids from water, resulting in exceptionally pure water with a TDS reading of zero parts per million (ppm). This process is vital for industries requiring water of the highest purity standards, ensuring optimal performance and quality in their processes and products

Applications of Ultra-Pure Demineralized Water
The applications of ultra-pure demineralized water span across various industries, including but not limited to:
- Semiconductor Industry: Critical for cleaning semiconductor wafers and manufacturing integrated circuits.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Essential for drug formulation, laboratory analysis, and equipment cleaning.
- Power Generation: Utilized in steam generation, cooling systems, and boiler feedwater.
- Laboratory Applications: Vital for conducting precise experiments and maintaining instrument integrity.
Advantages of Ultra Pure Demineralized Water Treatment
The adoption of ultra-pure demin water DI treatment offers numerous benefits to industries, including:
- Enhanced Product Quality: Minimizes impurities that could compromise the quality and performance of end products.
- Improved Equipment Performance: Prevents scaling and corrosion, extending the lifespan of equipment and reducing downtime.
- Reduction in Maintenance Costs: Decreases the frequency of equipment maintenance and replacements, leading to cost savings in the long run.
Ion Exchange Deionized Water: The Purification Process
Ion exchange deionization is a widely used method for producing demin water. In this process, water passes through ion exchange resins that selectively remove ions, including cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions). Through this exchange process, water is stripped of its mineral content, resulting in deionized water with extremely low conductivity and TDS levels.
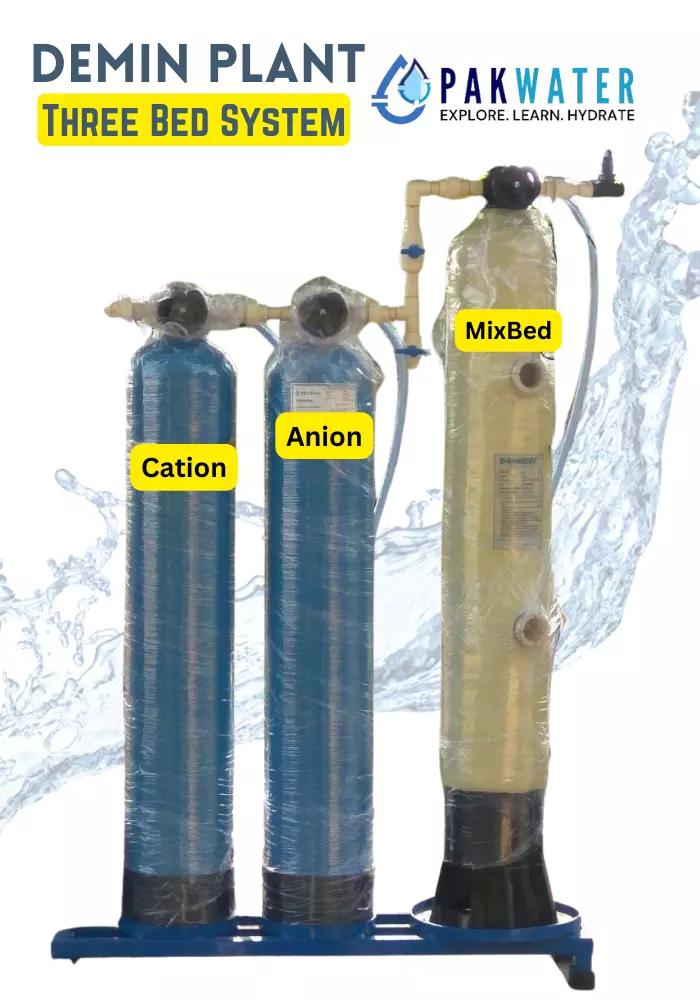
Mixed Bed Demineralized Water Treatment: Enhancing Purity
Mixed bed demineralized water treatment furthers the purification process by combining cation and anion exchange resins in a single vessel. This advanced method ensures maximum ion removal, resulting in water with unparalleled purity levels, ideal for applications demanding zero TDS water.

Limitations of Demineralizer (Mixbed) Systems
It’s crucial to note that demineralized (MixBed) systems have limitations regarding the quality of raw water they can effectively treat. The raw water TDS should be less than 270 ppm for optimal performance. However, when faced with higher TDS levels, alternative solutions such as Reverse Osmosis (RO) plants with pre-treatment become necessary.
Solution for Higher TDS Raw Water: RO Plant with Pre-Treatment
When the raw water TDS exceeds the recommended demineralization levels, installing an RO plant with pre-treatment becomes imperative. This integrated system combines the filtration capabilities of RO technology with pre-treatment processes to target higher TDS levels effectively.
RO Plant + Demin (Mixbed) Plant: A Comprehensive Solution
Combining an RO plant with pre-treatment followed by a demineralizer (mixbed) plant offers a comprehensive solution for treating raw water with elevated TDS levels. This integrated approach ensures ultra-pure water production tailored to the specific requirements of diverse industries.
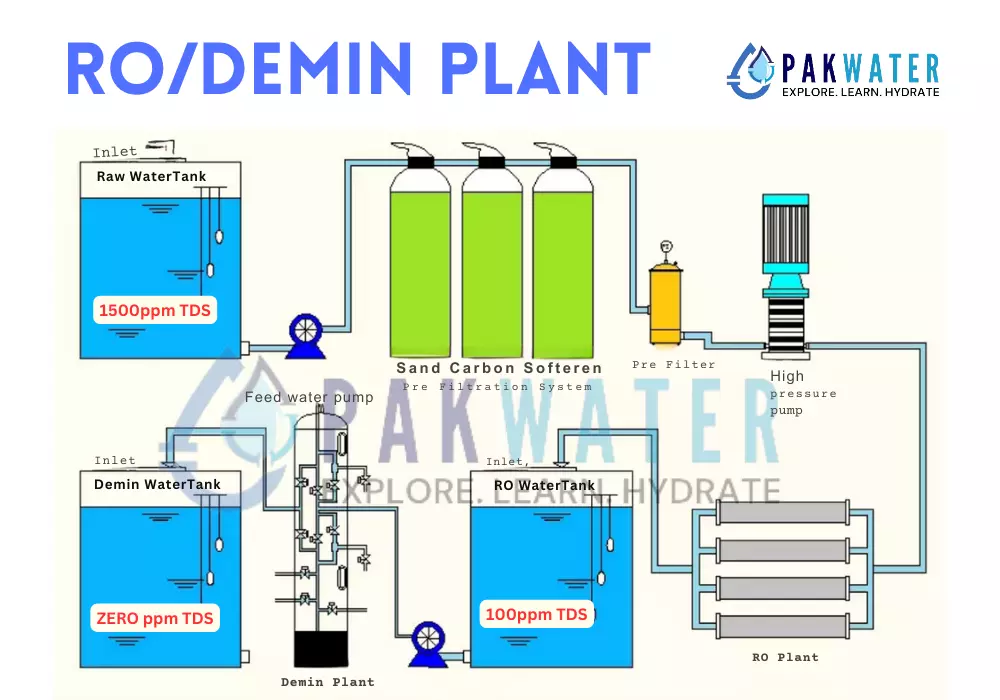
Raw Water Analysis:
Raw Feed Water TDS: 1500 ppm
Output Flow Requirement: 500 Liters Per Hour

Stage 1: Pre-Treatment
- Multimedia Filtration
- Dual Stage 5 Micron Cartridge Filter
- Process: Prepares raw water for RO treatment by removing large particles and impurities.

Stage 2: Reverse Osmosis (RO Plant)
- Components: HP Pump, RO TFC Membranes, Membrane Vessel
- Process: Purifies water, reducing TDS from 1500 ppm to approximately 100 ppm, suitable for demineralization

Stage 3: Demineralizer (Mixbed) Plant
- Process: Utilizes ion exchange resins to purify water further, achieving zero ppm TDS and ultra-pure water output
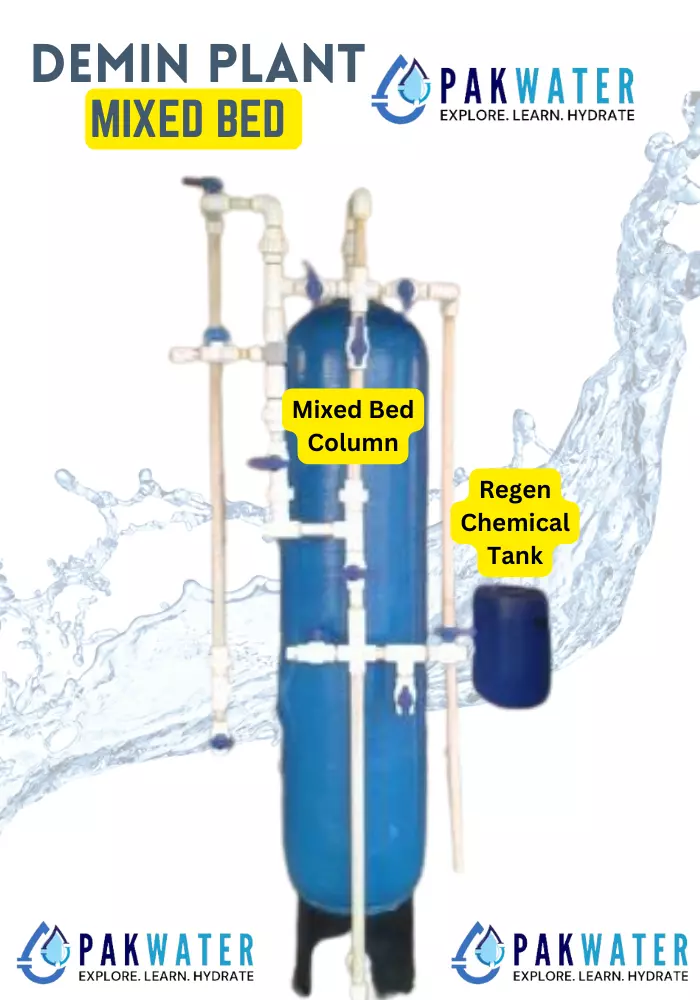
Regeneration Process and Chemical Requirements
Maintaining the efficiency of demineralized plants requires periodic regeneration and replenishment of regeneration chemicals:
- Regeneration Chemicals: Hydrochloric Acid, Sodium Hydroxide
- Process: Regeneration involves chemical treatment and media reactivation, ensuring the continued performance of the demineralization system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What industries benefit from ultra-pure zero TDS demineralized water?
- Industries such as pharmaceuticals, battery manufacturing, electroplating, dialysis, food processing, and injection molding rely on ultra-pure water for critical processes.
- How does demineralized water differ from other types of purified water?
- Demineralized water undergoes rigorous purification to remove all ions and dissolved solids, resulting in water of the highest purity with zero TDS.
- What are the advantages of RO plants with pre-treatment?
- RO plants with pre-treatment offer efficient removal of dissolved solids from high TDS raw water, ensuring optimal performance of downstream demineralization processes.
- How often should demineralized plants be regenerated?
- Demineralizer plants should be regenerated per the prescribed schedule based on water usage and quality parameters to maintain consistent water purity.
- What role do regeneration chemicals play in demineralized maintenance?
- Regeneration chemicals such as hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are essential for media reactivation and regeneration, ensuring the continued effectiveness of the demineralization process.
- Can demineralized plants be customized for varying water requirements?
- Yes, demineralized plants can be designed and customized based on specific water quality and quantity requirements, offering flexibility and scalability for diverse applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, achieving ultra-pure zero TDS demineralized water is indispensable for various industries requiring water of the highest purity standards. Industries can ensure optimal performance and quality in their operations by understanding the processes involved, from ion exchange deionization to mixbed demineralization, and implementing comprehensive treatment solutions.